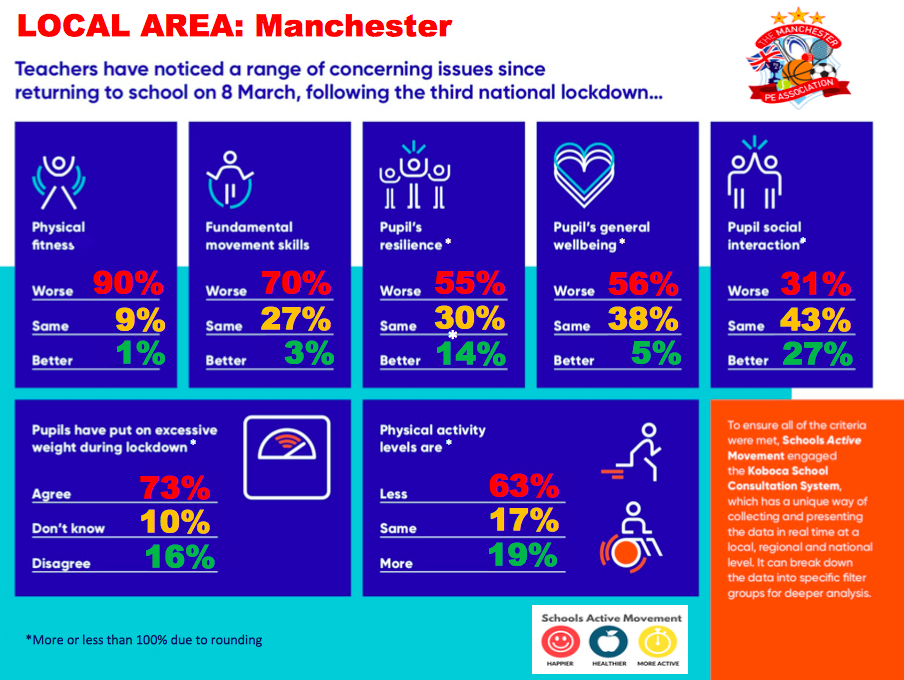
The “horrific” impact of the third national lockdown has been laid bare in a major new study which identified a major decline in children’s physical fitness and two thirds thought that pupils had gained excessive weight.
“The stark picture painted by this research reinforces the huge toll the pandemic has taken on young people’s wellbeing and why a focus on sport and activity needs to be an essential part of their recovery” said Ali Oliver, the CEO of the Youth Sports Trust.
This is the largest analysis of how the winter lockdown impacted young people, also records alarming drops in pupil resilience, activity levels, social interaction and fundamental movement skills.
School leaders are now actively prioritising physical activity during the summer term, but the findings will amplify calls for a long-term national strategy and future guarantees over the £320 million PE and Sport Premium. This is an annual payment which is ringfenced to improve the provision of PE, school sport and physical activity levels in primary schools, whether through staff training, specialist coaching or resources.
Of 2,647 schools (85 Manchester schools) that were surveyed, teachers were asked to score how children had returned from nine weeks of lockdown between January 4 and March 8 according to a series of key physical and emotional measurements.
On the physical, 84 per cent of schools judged that children had experienced a decline in fitness, 66 per cent said that children had gained excessive weight and 67 per cent recorded a regression of pupils’ fundamental skills and movement.
Almost two-thirds of schools judged children to have a lower resilience and 60 per cent reported that the general wellbeing of pupils had regressed against an improvement of only 5 per cent.
The survey data also found that children in urban communities were more likely to have been impacted than those in rural areas surrounded by more open space.